Tools for Managing Through Interpersonal Conflict
As students protest across campuses, faculty can help them manage through conflict. Here are two tools from the text chapter, “Communicating Across Differences,” and a few thoughts about character.
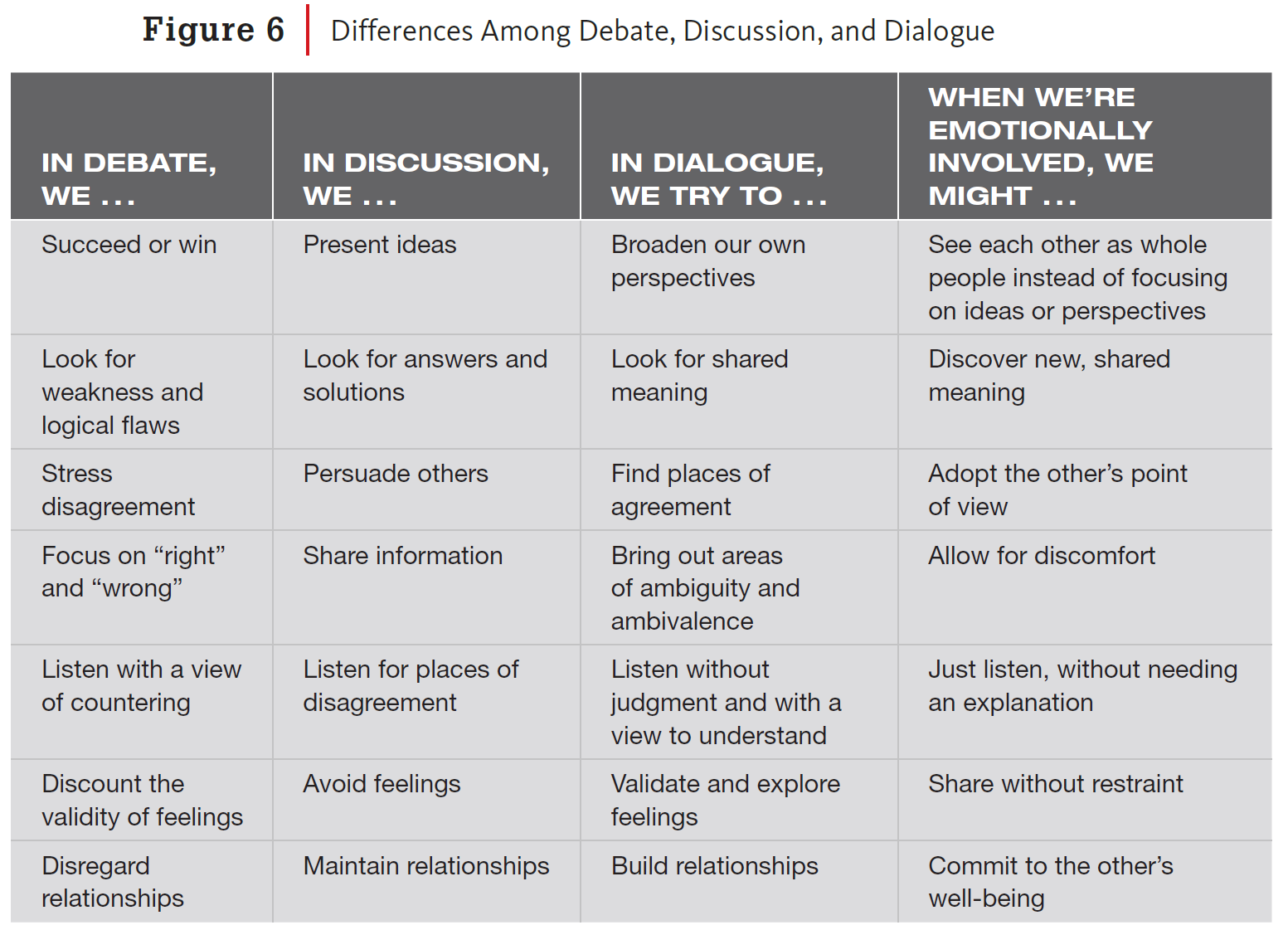
This matrix, adapted from other sources (see below), shows students how to move from debate to dialogue—and through emotional involvement, my addition for more personal and community conflicts.
Students may practice reflection after presentations or activities, but reflecting “in action” is a way to zoom out and get perspective during an interaction that isn’t going well. Questions about emotional and physical reactions deepen students’ typical intellectual reflections in the classroom and encourage students to take action—even to support those who disagree with them.
Students also will learn from discussions about character. When they stand for their beliefs, they demonstrate courage, but changing their beliefs also takes courage (and humility). Protests also may veer from challenging injustice to self-righteousness, an extreme of courage that looks like moral superiority and absolute certainty.
Protesting demonstrates compassion for one side, but so does seeing the other side’s pain. In addition, students are vulnerable when they protest: they risk emotional exposure and being “doxxed,” identity exposure they might consider unbearable.
Figure 6 is adapted from “Creating Community Across Difference,” Intergroup Dialogue Project, Cornell University, 2018, which is adapted from University of Michigan Program on Intergroup Relations, 2008. Original source: Daniel Yankelovich, The Magic of Dialogue: Transforming Conflict into Cooperation (New York: Simon & Schuster, 1999). Adapted with Eric Clay, multi-faith and secular chaplain.